Flood Watch for the Northern Rivers and Central West
Issued at 12:21 pm EST on Thursday 12 May 2022
Flood Watch Number: 3
MINOR FLOODING POSSIBLE IN THE NORTHERN RIVERS AND CENTRAL WEST FROM THURSDAY
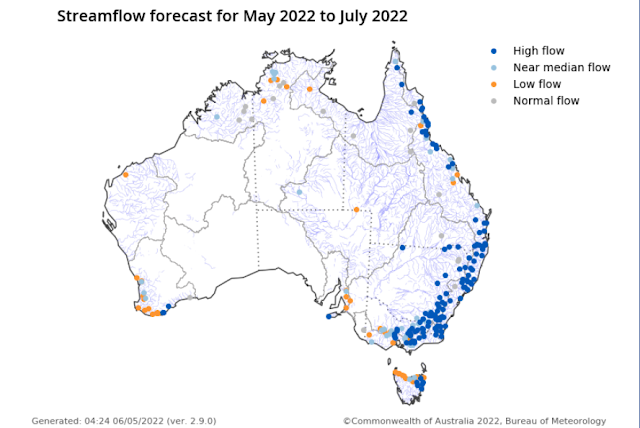
A trough over western inland New South Wales will generate further moderate to heavy rain in many areas of the Central West on Thursday. This may cause minor flooding along the Castlereagh, Macquarie and Bell Rivers from Thursday night.
* Reissue to include Castlereagh *
River level rises have been observed from recent moderate rainfall in the Northern Rivers. Further moderate showers expected on Thursday may see river levels rise to minor flood levels.
Renewed minor flooding is also possible along the Bogan River where a flood warning is current.
The Bureau is continuing to monitor the situation and will issue further catchment specific warnings if and when required.
Catchment soil moisture is average.
The weather system is expected to cause flooding for the catchments listed. Flood Classes (minor, moderate, major) are only defined for catchments where the Bureau provides a flood warning service.
Catchments likely to be affected include:
Tweed and Rouse Rivers - minor flooding
Brunswick River and Marshalls Creek - minor flooding
Wilsons River - minor flooding
Richmond River - minor flooding
Castlereagh River - minor flooding
Orange, Molong and Bell River - minor flooding
Turon and Macquarie Rivers to Burrendong Dam - minor flooding
Macquarie River d/s Burrendong Dam - minor flooding
Flood warnings are current for the Culgoa, Bokhara, Bogan, Paroo and Warrego Rivers.
For the latest flood and weather warnings see www.bom.gov.au/nsw/warnings/
For the latest rainfall and weather forecasts see www.bom.gov.au/australia/meteye/
For the latest rainfall and river level information see www.bom.gov.au/nsw/flood
[my yellow highlighting]
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
There is a chance of above median rainfall across much of the continent from 14 May 2022 to September 2022.
According to BOM long range forecasting there is also a 50-60% chance of the Page and Richmond electorates in the Northern Rivers region being “unusually wet” between 14 to 27 May 2022.
 |
| Click on image to enlarge |
Issued: 5 May 2022
Winter (June to August) rainfall is likely to be above median for most of Australia, except south-western Australia, the south-east coast, and southern Tasmania which have roughly equal chances of being above or below median.
June to August maximum temperatures are likely to be above median for northern, south-western, and south-eastern parts of Australia, but below median for broad areas of inland southern and central Australia.
Minimum temperatures for June to August are very likely to be warmer than median across almost all of Australia.
The weakening La Niña, the chance of a negative Indian Ocean Dipole, and other localised drivers are likely to be influencing this outlook.
Latest Climate Driver Update, 10 May 2022:
La Niña maintains strength
The 2021–22 La Niña event continues in the tropical Pacific, with little change in strength in the past few weeks.
Several indicators of La Niña, including tropical Pacific sea surface temperatures, cloudiness near the Date Line, and the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), have maintained or slightly increased their strength over the past fortnight. However, beneath the surface of the tropical Pacific, waters have warmed closer to neutral El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) levels.
Most climate models surveyed by the Bureau indicate a return to neutral ENSO by the early southern hemisphere winter. Only one of seven models continues La Niña conditions through the southern winter. La Niña conditions increase the chances of above average rainfall for much of eastern Australia, while neutral ENSO has little influence on rainfall patterns.
The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is neutral. All climate model outlooks surveyed suggest a negative IOD may develop in the coming months. While model outlooks have low accuracy at this time of year and hence some caution should be taken with IOD outlooks beyond May, there is strong forecast consistency across international models. A negative IOD increases the chances of above average winter–spring rainfall for much of Australia. It also increases the chances of warmer days and nights for northern Australia.
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) index is currently positive and is forecast to remain positive for the coming four weeks. During autumn SAM typically has a weaker influence on Australian rainfall, but as we approach winter, positive SAM often has a drying influence for parts of south-west and south-east Australia.
The Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) has recently strengthened in the western Indian Ocean. Most climate models indicate the MJO will briefly weaken, and then re-strengthen again later this week in the Maritime Continent or western Pacific region. Should the MJO re-strength in the Maritime Continent region, it can enhance rainfall in north-eastern Australia. It also typically increases cloudiness to Australia's north.
Climate change continues to influence Australian and global climate. Australia's climate has warmed by around 1.47 °C for the 1910–2020 period. Southern Australia has seen a reduction of 10–20% in cool season (April–October) rainfall in recent decades. There has also been a trend towards a greater proportion of rainfall from high intensity short duration rainfall events, especially across northern Australia. [my yellow highlighting]















