Showing posts with label funding. Show all posts
Showing posts with label funding. Show all posts
Thursday, 14 April 2016
With rates of domestic violence & sexual assault higher than the NSW average, the Northern Rivers region remains a target for federal funding cuts
The geographic area of the Northern NSW Local Health District extends from the Tweed Local Government Area (LGA) on the Queensland/NSW border in the north to the Clarence Valley LGA in the south, the Great Dividing Range in the west and the Pacific Ocean coastline in the east. The Northern NSW LHD covers a geographic region of 21,470 square kilometres with a total population in 2011 of 288,241 persons and is made up of seven LGAs and one smaller State Suburb (SSC). [Northern NSW LHD, Fact Sheet 1, July 2015]
This health district population was projected to reach over 300,000 in 2016.
One of the health issues it deals with is domestic and family violence, as do the local courts.
Between October 2014 to September 2015 in NSW the rate of domestic assault incidents per 100,000 head of population was 398.7.
For the corresponding period in the Northern NSW LHD the domestic assault rate was:
Richmond Valley Local Government Area – 550.6
Lismore Local Government Area – 478.8
Clarence Valley Local Government Area – 426.5
Tweed Local Government Area – 401.7
Kyogle Local Government Area – 399.0
Byron Local Government Area – 313.3
Ballina Local Government Area – 246.3
All but two local government areas were above the state average – four were significantly higher.
Five out of seven of these local government areas also exceeded the NSW rate for sexual offence incidents – Richmond Valley, Lismore, Clarence Valley, Byron and Ballina.
Yet this region remains a target for Abbott-Turnbull Government cuts to services used by victims of domestic violence and sexual assault.
The Northern Star reported on 8 April 2016:
SHADOW Attorney General Mark Dreyfus and Labor candidate for Page Janelle have backed the Northern Rivers Community Legal Centre's plea to have funding cuts to programs aimed at preventing domestic violence reversed.
They said the Federal Government had announced a third, or $30 million, of commonwealth funding would be cut to the 39 Community Legal Centres around the state as well as the scrapping of $100,000 per year in funding to the Lismore centre, introduced by Mr Dreyfus in 2013.
Mr Dreyfus said the cuts could mean the end of the Lismore-based centre's outreach service in Casino, as well as the possible closure of the Tweed office and the loss of a specialised family violence solicitor.
Northern Rivers Community Legal Centre acting centre manager Fia Norton said it was the biggest challenge in the centre's 20-year history.
"They're (the cuts) going to affect the most vulnerable people in our community," she said……
Ms Saffin said she was concerned the federal funding cuts would impact complimentary services to the State Government's Safer Pathways domestic violence program, a service NRCLS was selected to coordinate in Tweed in 2015.
"Last year the Northern Rivers CLC was selected by the NSW Government as one of five sites to roll out the Safer Pathways reforms for Domestic Violence, an integrated response service to prevent domestic violence deaths and serious injury to women and children," she said.
"But how will the program be impacted when cuts come into effect next year?.....
The cuts are set to come into effect in mid-2017.
Saturday, 23 January 2016
Live in the Tweed Valley? Want to help save a vital local women's service? Then read on....
Federal Labor MP for Richmond Justine Elliot on Facebook, Wednesday 20 January 2016, calling for people in the Tweed Valley to door knock a petition to save Tweed Valley Women’s Service and thirteen local jobs:
Here’s the link to my Petition http://bit.ly/1njNOu8 calling for the Nationals to restore NSW Government funding for the Tweed Valley Women’s Service. Please return the completed originals to my office at:
PO Box 6996
Tweed Heads South
NSW 2486
For these Petitions to be submitted the NSW Parliament requires the following:
• the person signing must be a Resident/Citizen of NSW
• NO FAXES of signed petition
• NO PHOTOCOPIES of signed petition
• ONLY ORIGINALS will be accepted
• Every signature must be original hand-writing, and signatures must not be pasted on, photocopied or transferred in any other way.
PO Box 6996
Tweed Heads South
NSW 2486
For these Petitions to be submitted the NSW Parliament requires the following:
• the person signing must be a Resident/Citizen of NSW
• NO FAXES of signed petition
• NO PHOTOCOPIES of signed petition
• ONLY ORIGINALS will be accepted
• Every signature must be original hand-writing, and signatures must not be pasted on, photocopied or transferred in any other way.
Text of petition:
Labels:
Baird Government,
funding,
government policy,
people power,
women
Wednesday, 22 April 2015
Tony Abbott and his attempts to degrade scientific research in Australia
It is well known that Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott believes that climate change science is absolute crap, but even he has exceeded expectations of what his passive-aggressive brand of climate change denialism will bring forth when he appointed self-described climate policy sceptic,
BRIEF BACKGROUND
Excerpt from one of the Lomborg Errors documents:
"The Skeptical Environmentalist" has given rise to extensive public discussion and debate, both in Denmark and internationally. There have been enthusiastic reviews in some of the world's top newspapers such as the Washington Post and the New York Times, and in The Economist.
The magazine Scientific American asked four leading experts to assess Bjørn Lomborg's treatment of their own fields: global warming, energy, population and biodiversity, devoting 11 pages to this in January 2002.
Stephen Schneider: "Global Warming, Neglecting the Complexities"
Schneider is a particularly respected researcher who has been discussing these problems for 30 years with thousands of fellow scientists and policy analysts in myriad articles and formal meetings.
Most of Bjørn Lomborg's quotes allude to secondary literature and media articles. Bjørn Lomborg uses peer-reviewed articles only when they support his rose-coloured point of view. By contrast, the authors on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) were subjected to three rounds of audits by hundreds of external experts.
Bjørn Lomborg employs no clear and discrete distinction between various forms of probabilities. He makes frequent use of the word "plausible" but, strangely for a statistician, he never attaches any probability to what is "plausible". IPCC gives a large "range" for the majority of projections, but Bjørn Lomborg selects the least serious outcomes.
Stephen Schneider then provides a specific criticism of Bjørn Lomborg's four main arguments:
1. Climate Science: Bjørn Lomborg quotes an article in Nature (from the Hadley Center, 1989), uncritically and without the authors' caveats. BL quotes Lindzen's controversial "iris effect" as evidence that IPCC's climate range needs to be reduced by a factor of almost three. BL either fails to understand this mechanism or else omits to state that the data stem from only a few years' data in a small part of a single ocean. Extrapolating this sample to the entire globe is wrong. Similarly, he quotes a controversial Danish paper claiming that solar magnetic events can modulate cosmic radiation and produce a clear connection between global low-level cloud cover and incoming cosmic rays as an alternative to CO2 in order to explain climate change. The reason IPCC discounts this theory is "that its advocates have not demonstrated any radiative forcing sufficient to match that of much more parsimonious theories, such as anthropogenic forcing."
2. Emissions scenarios: Bjørn Lomborg assumes that over the next several decades, improved solar machines and other new technologies will crowd fossil fuels off the market, which will be done so efficiently that the IPCC scenarios vastly overestimate the chance of major increases in CO2. This is not so much analysis as wishful thinking contingent on policies capable of reinforcing the incentives for such development, and BL is opposed to such policies. No credible analyst can just assert that a fossil-fuel-intensive scenario is not "plausible" and, typically, BL gives no probability that this might occur.
3. Cost-benefit calculations: Bjørn Lomborg's most egregious distortions and feeblest analyses are his citations of cost-benefit calculations. First, he chides the governments that modified the penultimate draft of the IPCC report. But there was a reason for that modification, which downgraded aggregate cost-benefit studies: these studies fail to consider so many categories of damage held to be important by political leaders, and it is therefore not the "total cost-benefit" analysis that Bjørn Lomborg wants. Again, BL cites only a single value for climate damage - 5 trillion dollars - although the same articles indicate that climate change can vary from benefits to catastrophic losses. It is precisely because the responsible scientific community cannot rule out catastrophic outcomes at a high level of confidence that climate mitigation policies are seriously proposed. For some inexplicable reasons, BL fails to provide a range of climate damage avoided, only a range for climate policy costs. This estimate is based solely on the economics literature but ignores the findings of engineers and does not take into account pre-existing market imperfections such as energy-inefficient machinery, houses and processes. Thus, five US Dept. of Energy laboratories have suggested that such a substitution can actually reduce some emissions at below-zero costs.
4. The Kyoto Protocol: Bjørn Lomborg's invention of a 100-year regime for the Kyoto Protocol is a distortion of the climate policy process. Most analysts know that "an extended" Kyoto Protocol cannot deliver the 50% reduction in CO2 emissions needed to prevent large increases at the end of the 21st century and during the 22nd century, and that developed and developing countries alike will have to cooperate to fashion cost-effective solutions over time. Kyoto is a starting point, and yet with his 100-year projection BL would squash even this first stage.
Bjørn Lomborg's book is published by the social sciences side of Cambridge University Press. It is no wonder, then, that the reviewers failed to spot BL's unbalanced presentation of the natural science. It is a serious omission on the part of an otherwise respected publishing house that natural-science researchers were not taken on board. "Lomborg admits, 'I am not myself an expert as regards ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS' - truer words are not found in the rest of the book".
John P. Holdren: "Energy: Asking the Wrong Questions"
Bjørn Lomborg's chapter on energy covers a scant 19 pages and is devoted almost entirely to attacking the belief that the world is running out of energy, a belief that BL appears to regard as part of the "environmental litany". But only a handful of environmental researchers, if any at all, believe this today. Conversely, what they do say about this topic is that we are not running out of energy, but out of environment, i.e. the capacity of air, water, soil and biota to absorb, without intolerable consequences for human well-being, the effects of energy extraction, transport, energy transformation and energy use. They also say that we are running out of the ability to manage other risks of the energy supply, such as overdependence on Middle East oil and the risk of nuclear energy systems leaking weapons materials and expertise into the hands of proliferation-prone nations or terrorists. This has been the position of the environmental researchers for decades (e.g. from 1971, 74, 76 and 77).
So whom is BL so resoundingly refuting with his treatise on the abundance of world energy resources? The professional analysts have not been arguing that the world is running out of energy, only that the world could run out of cheap oil. BL's dismissive rhetoric notwithstanding, this is not a silly question, nor one with an easy answer.
Oil is currently the most valuable of the conventional fossil fuels that have long provided the bulk of the world's energy, including almost all energy for transport. The quantity of recoverable oil resources is thought to be far less than coal and natural gas, and those reserves are located in the politically volatile Middle East. Much of the rest is located offshore and in other difficult and environmentally fragile areas. There is, accordingly, a serious technical literature, produced mainly by geologists and economists, exploring the questions of when world oil production will peak and begin to decline, and what the price might be in 2010, 2030 or 2050 - with considerable disagreement among informed professionals.
BL seems not to recognize that the transition from oil to other sources will not necessarily be a smooth one or occur at prices as low as the price of oil today. BL shows no sign of understanding why there is real debate about this among serious-minded people.
BL offers no explanation of the distinction between "proved reserves" and "remaining ultimately recoverable resources", nor of the fact that the majority of the latter category is located in the Middle East, but placidly informs us that it is "imperative for our future energy supply that this region remains reasonably peaceful" - as if that observation does not undermine any basis for complacency.
BL is right in his basic proposition that the resources of oil, oil shale, nuclear fuels and renewable energy are immense. But that is disputed by only few environmental researchers-and no well-informed ones. But his handling of the technical, economic and environmental factors that will govern the circumstances and quantities in which these resources might actually be used is superficial, muddled and often plain wrong. His mistakes include apparent misreadings and misunderstandings of statistical data, the very kinds of errors he claims are pervasive in the writings of environmentalists. By the same token, there are other elementary blunders of a type that should not be committed by any self-respecting statistician. Thus, it is wrong that measures in the developed countries have eliminated the vast majority of SO2 and NO2 from smoke from coal-burning facilities: it is only a minor proportion. Other examples are given, and when it comes to nuclear energy, plutonium is such a great security problem as regards the potential production of nuclear weapons that it may preclude use of the "breeding" approach unless a new technology is invented that is just as cheap.
BL uses precise figures, where there is no basis for such, and he produces assertions based on single citations and without detailed elaborations, which is far from representative of the literature.
Most of what is problematic about the global energy picture is not covered by BL in the chapter on energy but in the chapters dealing with air pollution, acid rain, water pollution and global warming. The latter has been devastatingly critiqued by Schneider.
There is no space to deal with the other energy-related chapters, but their level of superficiality, selectivity and misunderstandings is roughly consistent with what has been reviewed here.
"Lomborg is giving skepticism - and statisticians - a bad name."
John Bongaarts: "Population: Ignoring Its Impact"
Bjørn Lomborg's view that the number of people is not the problem is simply wrong. The global population growth rate has declined slowly, but absolute growth remains close to the very high levels observed in past decades. Any discussion of global trends is misleading without taking account of the enormous contrasts between world regions, where the poorest nations of Africa, Asia and Latin America have rapidly growing and young populations, whereas Europe, North America and Japan have virtually zero, and in some cases even negative, growth. As a consequence, all future growth will be concentrated in the developing countries, where four-fifths of the world's population lives: from 4.87 to 6.72 billion between 2000 and 2025, or just as large as the record-breaking increase in the past quarter of the (21st) century. This growth in the poorest parts of the world continues virtually unabated. The growth has led to high population density in many countries, but BL dismisses concerns about this issue, based on a simplistic and misleading calculation of density as the ratio of people to land. In Egypt this would make 88/km2, but deducting the uncultivated and unirrigated part of Egypt, it makes 2,000/km2 - no wonder Egypt has to import foodstuffs! Measured correctly, population densities have reached extremely high levels, particularly in large countries in Asia and the Middle East. This makes demands in terms of agricultural expansion on more difficult, hitherto untilled terrain, increased water consumption and a struggle for the scarce water resources between households, industry and farming. The upshot will be to make growth in food production more expensive to achieve. BL's view that increased food production is a non-issue rests heavily on the fact that foodstuffs are cheap; but BL overlooks the fact that it is large-scale subsidies to farmers, particularly in the developed countries, that keep prices artificially low.
Appreciably expanding farming will result in a reduction of woodland areas, loss of species, soil erosion, and pesticide and fertilizer run-offs. Reducing this impact is possible but costly, and would be easier if the growth in population were slower.
BL overlooks the fact that population growth contributes to poverty. First, children have to be fed, housed, clothed and educated - while economically non-productive - then jobs have to be created once they reach adulthood. Unemployment lowers wages to subsistence level. Counteracting population growth has fuelled "economic miracles" in a number of East Asian countries.
BL overlooks the fact that the favourable trend in life expectancy is due to intensive efforts on the part of governments and the international community, but despite this, 800 million are still malnourished and 1.2 billion are living in abject poverty. Population is not the main cause of the world's social, economic and environmental problems, but it is a substantial contributory factor. If future growth can be slowed down, future generations would be better off.
Thomas Lovejoy: "Biodiversity: Dismissing Scientific Progress"
In less than a page, Bjørn Lomborg discounts the value of biodiversity both as a library for the life sciences and as a provider of ecosystem services (partly due to the general absence of markets for these services). When he does get round to extinction, he confounds the process by which a species is judged to have been made extinct with estimates and projections of extinction rates. In contrast to BL's claim, the loss of species from habitat remnants is a widely documented phenomenon. A number of factual errors are highlighted. BL takes particular exception to Norman Myer's 1979 estimate that 40,000 species are being lost every year, failing to acknowledge that Myer deserves credit for being the first to point out that the number was large and at a time when it was difficult to do so accurately. Current estimates are given in terms of the increases over normal extinction rates. BL cynically spurns this method, because such estimates sound more ominous. Instead, he ought to acknowledge that this method is an improvement in the science. These rates are currently 100 to 1,000 times' the normal, and are certain to rise as natural habitats continue to dwindle.
The chapter on acid rain is equally poorly researched and presented. BL establishes that acid rain has nothing to do with urban pollution, though it is a fact that nitrogen compounds (NOx) from traffic are a major source. Errors are pointed out in BL's view of acid rain on forests.
The chapter on forests suffers from BL not knowing that FAO's data are marred by the weight of so many different definitions and methods that any statistician should know they are not valid in terms of a time series. There are errors in the figures from Indonesia in 1997. BL confuses forests with tree plantations, and asserts that the only value of forests is harvestable trees. That is analogous to valuing computer chips for their silicon content only.
It is important to know that while deforestation and acid rain are reversible, extinction of species is not.
BL entirely overlooks the fact that environmental scientists identify a problem, posit hypotheses, test them and, having reached their conclusions, suggest remedial policies. By focusing on the first and last stages in this process, BL implies incorrectly that all environmentalists do is exaggerate.
Dr
Peter Raven, President of the American Association for the Advancement of
Science in 2002 said of Lomborg: "...he's not an environmental scientist
and he doesn't understand the fields that he's talking about so in that case,
if you have a point to make and you want to get to that point, which is:
everything's fine, everybody's wrong, there is no environmental problem, you
just keep making that point. It's like a school exercise or a debating society,
which really doesn't take into account the facts".
"Raven
said that the success of Lomborg's book 'demonstrates the vulnerability of the
scientific process -- which is deliberative and hypothesis driven -- to
outright misrepresentation and distortion.'"
Newsweek 21 February 2010:
Lomborg
opens Cool It with a long
discussion on polar bears, arguing that no more than two (of 20) groups are
declining in population, that their numbers are not falling overall, and, in
places where they are, that it is not a result of global (or Arctic) warming.
In fact, polar-bear populations in warming regions are rising, he argues,
suggesting that a warmer world will be beneficial to the bears. As Friel shows,
Lomborg sourced that to a blog
post and to a study that never mentioned polar bears. But he
ignored the clear message of the most authoritative assessment of the bears'
population trends, namely, research
by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. It found that bear
populations are indeed declining where the Arctic is warming. In fact,
concluded the IUCN, polar-bear populations "have declined
significantly" where spring temperatures have risen dramatically. It also
offered an explanation for Lomborg's claim that numbers are falling most where
temps are getting colder: that area happens to be where there is unregulated
hunting.
For
his claim that the polar-bear population "has soared," Lomborg cited a 1999 study (scroll down to the paper by Ian
Stirling). But that study described declining birthrates and other threats
to the bears, blaming warmer spring temperatures that cause the sea ice to
break up. Overall, since the mid-1980s polar-bear numbers have fallen, which
experts attribute to global warming. The source is thus not exactly the solid
endorsement of Lomborg's claim about thriving polar bears that one might
assume.
Climate
Council
14 April 2015:
The
Australian Government today announced they would contribute $4m for Danish
climate contrarian Bjorn Lomborg to establish a new “consensus centre” at the
University of Western Australia.
In the face of deep cuts to the CSIRO
and other scientific research organisations, it's an insult to Australia’s
scientific community.
As
the Climate Commission, we were abolished by the Abbott Government in 2013 on
the basis that our $1.5 million annual operating costs were too expensive. We
relaunched as the Climate Council after thousands of Australians chipped in to
the nation’s biggest crowd-funding campaign…
It
seems extraordinary that the Climate Commission, which was composed of Australia’s best climate scientists,
economists and energy experts, was abolished on the basis of a lack of
funding and yet here we are three years later and the money has become
available to import a politically-motivated think tank to work in the same
space.
This
is why the work of the Climate Council is so important - to counter this continuing ideological
attempt at deceiving the Australian public.
Mr
Lomborg’s views have no credibility in the scientific community. His message
hasn’t varied at all in the last decade and he still believes we shouldn't take
any steps to mitigate climate change. When someone is unwilling to adapt their
view on the basis of new science or information, it's usually a sign those views are politically motivated.
He
further states that he has an M.A. in political science (University of Aarhus)
and a Ph.D. in political science (University of Copenhagen).
His degrees are in social science and not in any of the scientific disciplines which inform credible climate research.
Labels:
Abbott spin-cycle,
climate change,
funding,
government policy,
science
Tuesday, 21 April 2015
Mental health report and recommendations that the Abbott Government didn't want you to see until it had worked out how to pass the buck to the states
Australian Health Minister Sussan Ley has had the four-volume National Review of Mental Health Programmes and Services since 1 December 2014.
Despite the report being leaked to Crikey, she insisted on 15 April 2015 that; there was no sense in releasing the report before the Government had formulated a response.
On 19 April Crikey Insider sent out access links to all four volumes to its readers.
The Abbott Government has now released the full report which can be read at leisure on the Mental Health Commission website.
The report makes 25 recommendations:
Summary
of recommendations
1.
Set clear roles and accountabilities to shape a person-centred mental health
system
Rec 1. Agree the Commonwealth’s role in mental health is through
national leadership
and
regional integration, including integrated primary and mental health care.
Rec 2. Develop, agree and implement a National Mental Health and Suicide Prevention
Plan with
states and territories, in collaboration with people with lived
experience,
their families and support people.
Rec 3. Urgently clarify the eligibility criteria for access to
the National Disability
Insurance
Scheme (NDIS) for people with disability arising from mental illness
and
ensure the provision of current funding into the NDIS allows for a significant
Tier
2 system of community supports.
2.
Agree and implement national targets and local organisational performance
measures
Rec 4. Adopt a small number of important, ambitious and
achievable national targets
to
guide policy decisions and directions in mental health and suicide prevention.
Rec 5. Make Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health
a national priority and
agree
an additional COAG Closing the Gap target specifically for mental health.
Rec 6. Tie receipt of ongoing Commonwealth funding for
government, NGO and
privately
provided services to demonstrated performance, and use of a single
care
plan and eHealth record for those with complex needs.
3.
Shift funding priorities from hospitals and income support to community and
primary health care services
Rec 7. Reallocate a minimum of $1 billion in Commonwealth acute
hospital funding in
the
forward estimates over the five years from 2017–18 into more community based
psychosocial,
primary and community mental health services.
Rec 8. Extend the scope of Primary Health Networks (renamed
Primary and Mental
Health
Networks – PMHNs) as the key regional architecture for equitable
planning
and purchasing of mental health programmes, services and integrated
care
pathways.
Rec 9. Bundle-up programmes and boost the role and capacity of
NGOs and other
service
providers to provide more comprehensive, integrated and higher-level
mental
health services and support for people, their families and supporters.
Rec 10. Improve service equity for rural and remote communities
through place-based
models
of care.
4.
Empower and support self-care and implement a new model of stepped care across Australia
Rec 11. Promote easy access to self-help options to help people,
their families and
communities
to support themselves and each other, and improve ease of
navigation
for stepping through the mental health system.
Rec 12. Strengthen the central role of GPs in mental health care
through incentives for
use
of evidence-based practice guidelines, changes to the Medicare Benefits
Schedule
and staged implementation of Medical Homes for Mental Health.
Rec 13. Enhance access to the Better Access programme for those
who need it most
through
changed eligibility and payment arrangements and a more equitable
geographical
distribution of psychological services.
Rec 14. Introduce incentives to include pharmacists as key
members of the mental
health
care team.
5.
Promote the wellbeing and mental health of the Australian community, beginning
with a healthy start to life
Rec 15. Build resilience and targeted interventions for families
with children, both
collectively
and with those with emerging behavioural issues, distress and
mental
health difficulties.
Rec 16. Identify, develop and implement a national framework to
support families and
communities
in the prevention of trauma from maltreatment during infancy and
early
childhood, and to support those impacted by childhood trauma.
Rec 17. Use evidence, evaluation and incentives to reduce stigma,
build capacity and
respond
to the diversity of needs of different population groups.
6.
Expand dedicated mental health and social and emotional wellbeing teams for
Aboriginal
and Torres Strait Islander people
Rec 18. Establish mental health and social and emotional
wellbeing teams in Indigenous
Primary
Health Care Organisations (including Aboriginal Community-Controlled
Services),
linked to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander specialist mental health
services.
7.
Reduce suicides and suicide attempts by 50 per cent over the next decade
Rec 19. Establish 12 regions across Australia as the first wave
for nationwide
introduction
of sustainable, comprehensive, whole-of-community approaches to
suicide
prevention.
8.
Build workforce and research capacity to support systems change
Rec 20. Improve research capacity and impact by doubling the
share of existing and
future
allocations of research funding for mental health over the next five years,
with
a priority on supporting strategic research that responds to policy
directions
and community needs.
Rec 21. Improve supply, productivity and access for mental health
nurses and the
mental
health peer workforce.
Rec 22. Improve education and training of the mental health and
associated workforce
to
deploy evidence-based treatment.
Rec 23. Require evidence-based approaches on mental health and
wellbeing to be
adopted
in early childhood worker and teacher training and continuing
professional
development.
9.
Improve access to services and support through innovative technologies
Rec 24. Improve emergency access to the right telephone and
internet-based forms of
crisis
support and link crisis support services to ongoing online and offline forms
of
information/education, monitoring and clinical intervention.
Rec 25. Implement cost-effective second and third generation
e-mental health solutions
that
build sustained self-help, link to biometric monitoring and provide direct
clinical
support strategies or enhance the effectiveness of local services.
support strategies or enhance the effectiveness of local services.
Labels:
Abbott Government,
funding,
health,
Health Services
Tuesday, 14 April 2015
Suicide is still the leading cause of premature death in Australia yet it took the Abbott Government ten months before it blinked over mental health funding cuts
In the May 2014 budget papers Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott, along with Treasurer Joe Hockey and Finance Minster Mathias Cormann, wielded an ideological razor on health funding provided by the Commonwealth .
It has taken the Abbott Government ten long months to realise that the mental health sector, a traditionally underfunded area, could only respond to mooted federal funding cuts by reducing services or closing agencies.
The Minister for Health Sussan Ley finally announced a funding extension for a further twelve months on 2 April 2015 - two days after an Australian Bureau of Statistics media release which confirmed that suicide was still the leading cause of premature death in Australia.
It's almost as though someone in the Prime Minister's office finally put two and two together and realised that there was a public relations disaster of monumental proportions in the offing.
BRIEF BACKGROUND
Excerpt
from an Australian Bureau of Statistics media release on 24 July 2010: New
South Wales was found to have the lowest suicide rate at 8.6 deaths per 100,000
people for the period 2006-2010.
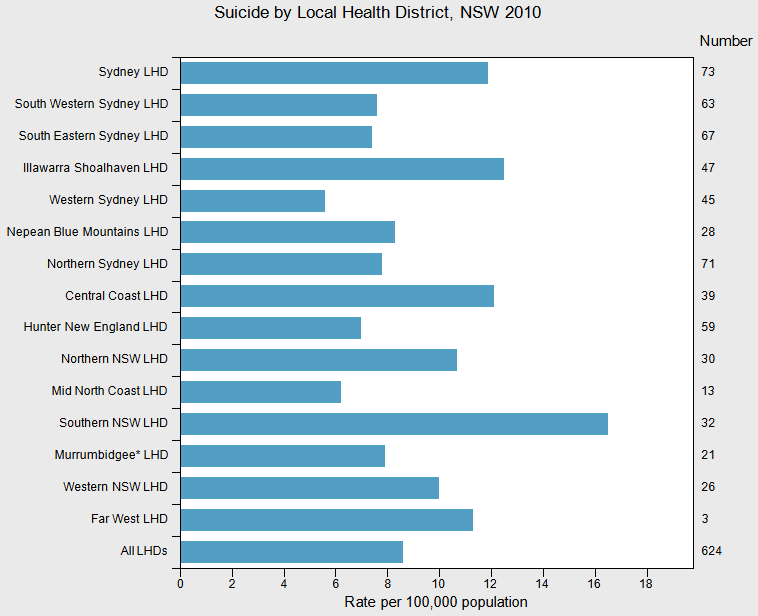
NSW
Government Suicide
by Local Health District and year:
The suicide rate for Northern NSW in 2010 was 10.7 deaths per 100,000 people and for the Mid-North Coast the rate was 6.2 per 100,000 people.
By 2013 New South Wales had a suicide rate of 9.1 per 100,000 people for 2009-2013.
In
2012-13 hospitalisation of young people aged between 15 and 24 years for
intentional self-harm was significantly higher than the state average in
Ballina, Byron, Clarence Valley and Coffs Harbour local government areas and, on
par with the state average in Kyogle, Lismore, Tweed and Richmond Valley
local government areas.
(a) All causes of death data from 2006 are subject to a revisions process - once data for a reference year are 'final', they are no longer revised. Affected data in this table are: 2009-2011 (final), 2012 (revised), 2013 (preliminary). See Explanatory Notes 52-54 and Technical Note, Causes of Death Revisions, 2011 and 2012.
(b) Includes ICD-10 codes X60-X84 and Y87.0. Care needs to be taken in interpreting figures relating to suicide. See Explanatory Notes 87-93. (c) Age-specific rates of deaths are the number of deaths per 100,000 population. See Glossary and Data used in calculating death rates (Technical Note) for further information. (d) The age-specific rates published in this table are calculated for the 2009-2013 reference period. As such, they may differ from age-specific rates published elsewhere in Causes of Death, which are calculated for a single year. (e) Includes deaths of persons whose age was not stated. | ||||||
(a) All causes of death data from 2006 are subject to a revisions process - once data for a reference year are 'final', they are no longer revised. Affected data in this table are: 2009-2011 (final), 2012 (revised), 2013 (preliminary). See Explanatory Notes 52-54 and Technical Notes, Causes of Death Revisions, 2011 and 2012.
(b) Cells with small values have been randomly assigned to protect the confidentiality of individuals. As a result, some totals will not equal the sum of their components. Cells with a zero value have not been affected by confidentialisation. (c) Includes ICD-10 codes X60-X84 and Y87.0. Care needs to be taken in interpreting figures relating to suicide. See Explanatory Notes 87-93. (d) Includes 'other territories'. (e) Includes deaths of persons whose age was not stated. | |||||||||
np not available for publication but included in totals where applicable, unless otherwise indicated.
|
The Sydney Morning Herald 8 December 2014:
Mental health organisations are cutting services and shedding staff because of uncertainty about their funding, according to the sector's peak body.
Forty per cent of mental health agencies say they have already lost staff as a result of the uncertainty, while more than half report a reduction in services to their clients, according to a survey of 75 organisations which receive Commonwealth funding, conducted by Mental Health Australia.
Almost half of those surveyed reported difficulty in attracting new staff, and 81 per cent reported a decline in staff morale.
Fifty six per cent of organisations said they had not had communications with the government regarding the future of their Commonwealth funding after June next year, and 85 per cent reported a loss of trust in government among management and staff.
Mental Health Australia chief executive Frank Quinlan said the typically short-term funding cycles for mental health programs, a lack of clarity about how the National Disability Insurance Scheme would affect funding arrangements, and a national review of existing mental health programs had combined to create a "perfect storm of indecision."
"Nobody argues about the need for these programs but at the moment we just can't seem to find anybody to own the future of that problem," Mr Quinlan said.
Health Minister Peter Dutton is considering the review of existing services, conducted by the National Mental Health Commission, after receiving the report late last month….
Excerpt from Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) media release, 31 March 2015:
Suicide was once again the leading cause of death for Australian's aged 15 to 44. Suicide accounted for 2,520 deaths in 2013 at a standardised death rate of 10.7 per 100,000 people. The median age at death for suicides is lower than for many other causes at 44.5 years of age. As a result, suicide accounted for over 85,000 years of life lost making it the leading cause of premature death in Australia. [my red bolding]
Ms Ley said the 12-month extension would allow services to continue to be delivered while work continued on the current Mental Health Review.
ABC News 2 April 2015:
In a move worth $300 million, mental health services will have their funding renewed for a further 12 months.
The announcement made today by Health Minister Sussan Ley follows a campaign by Mental Health Australia, after some mental health services began to shut down, unsure of future funding.
Hundreds of contracts were due to end on June 30.
Ms Ley said the 12-month extension would allow services to continue to be delivered while work continued on the current Mental Health Review.
Sunday, 1 March 2015
So who are these Americans thought willing to put "tens of millions" of dollars into Tony Abbott's re-election coffers?
It causes enough unease to know that a Conservative Party peer of the realm sitting in the U.K. House of Lords financed past Liberal Party of Australia federal election campaigns to the tune of $1.5 million, now it seems Americans are expected to donate to Tony Abbott’s 2016 re-election coffers.
The Sydney Morning Herald 24 February 2015:
Mr Higginson wrote that he had raised $70 million since 2011 and recently "laid out my plans to the PM" to travel to the United States to raise "tens of millions" from donors.
Is the Prime Minister so unpopular with home-grown donors that he now has to look elsewhere for the big money?
Or is this trawl for foreign political donations part of the Abbott Government's "open for business" approach to governing?
Friday, 6 February 2015
Shorter George Brandis: Don't waste your time contacting me, I'm not interested if you live in the Clarence Valley
For years accessing no-cost legal advice, mediation and support in the Clarence Valley has been a lottery to say the least.
Name any problem (tenancy issue, dispute with a neighbour, companion animal problems, family breakdown etc.) that is not actively before the courts and the individual concerned will only have telephone numbers for services situated a hundred, sometimes many hundreds of, kilometres away.
This sad little article in The Daily Examiner on 4 February 2015 clearly indicates why it is about to become even harder in Abbott's Australia:
The Northern Rivers Community Legal Centre (NRCLC) is left in limbo as it waits for the finalisation of funding cuts.
The NRCLC is the main provider of legal support in domestic violence, employment, credit debt and other areas to the Clarence Valley. It was set to open an office in the Richmond Valley which would have provided better access to Clarence Valley residents, however, funding cuts meant it could no longer go ahead.
"A lot of people suffering domestic violence would have been helped by that office," centre manager Angela Pollard said.
"At the moment everyone is flailing. We still don't know what is happening."
She said they kept receiving funding extensions to continue operating, however, that left them in suspense while they waited for the axe to fall.
Ms Pollard tried to lobby Federal Attorney-General George Brandis to not cut the funding for the office, but he replied by letter not to waste taxpayer dollars on lobbying.
Ms Pollard said she was pleased Australian of the Year Rosie Batty highlighted Prime Minister Tony Abbott's contradictory national scheme for domestic violence orders while funding to legal services were cut.
Labels:
Abbott Government,
Clarence Valley,
funding
Tuesday, 3 February 2015
So what type of jobs might Clarence Valley workers get from 155km of Pacific Highway upgrade?
In October 2014 the timeline Prime Minister Tony Abbott placed on completion of the Pacific Highway upgrade between Woolgoolga and the NSW-Qld border was by the "end of the decade", or to put in another way, by 2020.
All the larger contracts (with contract values ranging from $132.5 million down to less than $500,000) were either invitee only or advertised and, these have been awarded to firms from outside the Clarence Valley and sometimes out of the state for periods up to 2016 and 2017.
In all fairness most of these contracts were beyond the means of most Clarence Valley businesses because of the steep prequalification financial levels required to assure both the federal and state government co-funders of a contractor’s financial stability, solvency, and capacity to manage cash flow requirements.
So how are valley businesses going to benefit from the est. $220 million this approximately 155km upgrade (from 6km north of Woolgoolga to 6km south of Ballina) will cost?
Sadly, Clarence Valley Council let the cat out of the bag in its media release of 29 January 2014:
“While the exact contracts are unknown, we do know there will be opportunity for local businesses,”….
“Examples of opportunities this may present are; landscaping, cleaning, drainage, fencing, etc. [my red bolding]
There are currently only two open tenders available on the NSW eTendering website and these are for an Independent Hydrological Expert Service and Registration of Interest for the Design and Construction of the bridge over the Clarence River at Harwood, NSW. Even the emu fencing contract between Glenugie and Tyndale has passed valley businesses by.
There has also been talk of the jobs expected to be generated by the upgrade section between Glenugie to Grafton and Iluka-Maclean-Yamba, which includes a second bridge at Harwood.
There has also been talk of the jobs expected to be generated by the upgrade section between Glenugie to Grafton and Iluka-Maclean-Yamba, which includes a second bridge at Harwood.
With the valley-wide unemployment rate running at 8.1 per cent (Grafton 8.9 per cent and Maclean-Yamba-Iluka 7.8 per cent) and with negative employment growth in the September Quarter 2014, it would appear that Clarence Valley locals must pin their hopes on sub-contracting crumbs falling from the table once construction work commences or on finding grunt work with the major contractors, cross their fingers that some of those workers from elsewhere want local accommodation for the twelve to twenty-four months these companies might be working somewhere in the valley and, hope like hell that the Harwood Bridge construction - and the separately funded Grafton Bridge project* - begin by 2018.
* The NSW 2014-15 Budget Papers mention Grafton Bridge, with a foreshadowed $117 million in state funding without any specified timeline, but only $8 million actually available for bridge and feeder roads planning this financial year.
Friday, 19 December 2014
Just how big is the ABC's slice of the federal budget pie?
Business Spectator 20 November 2014:
When members of the Abbott Government talk about a need to rein in Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) spending, they rely on graphs like the one above (which displays funding in terms of millions of dollars) in order to scare voters about current and future public broadcasting sustainability.
Here is just a small visual reminder to the Abbott Government of how little, in the grand scheme of things, ABC television, radio and digital platforms actually cost.
A relatively small 0.271% of the total federal budget according to BudgetAus:
Labels:
Abbott Government,
ABC,
ABC radio,
ABC television,
budget,
funding
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)