“Australia isn’t experiencing a wage-price spiral, it’s at the beginning of a price-profit spiral,” said Australia Institute chief economist, Dr Richard Denniss.
“The national accounts show it is rising profits, not rising costs, that are driving Australia’s inflation. While workers are being asked to make sacrifices in the name of controlling inflation, the data makes clear that it is the corporate sector that needs to tighten its belt.”
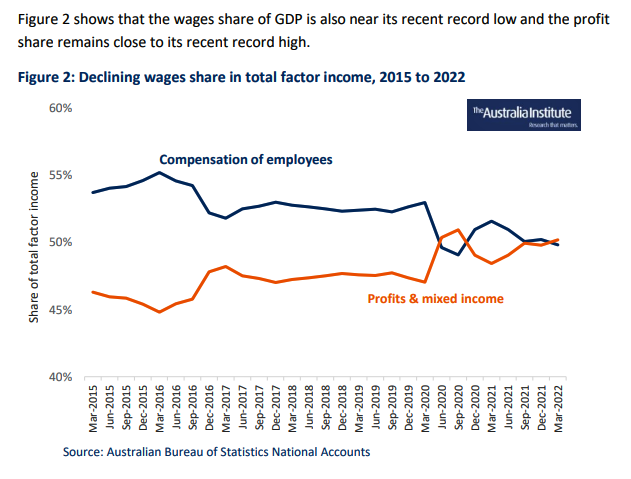
The report points out that wage growth was at record low levels, while the profit share was at a near-record share of GDP.”
[The Guardian, 18 July 2022]
Corporations are causing inflation by passing on price increases. They are doing this to protect and grow their profits, the same reason why they are refusing decent wage rises https://t.co/1imWMHBBEA
— Sally McManus (@sallymcmanus) July 17, 2022
The Australia Institute, Are wages or profits driving Australia’s inflation? An analysis of the National Accounts, July 2022, excerpts:
Introduction
In recent months the role of wages in driving inflation has been frequently discussed, with many commentators expressing concern that Australia risks a ‘wage price spiral’.
For example:
“Aggressive wages growth will only spur further inflation growth.”
— Andrew Mackellar, CEO of the Australian Chamber of Commerce and Industry
“We are now at risk of a wages and inflation and interest rates death spiral.”
— Innes Willox, CEO of Australian Industry Group
“In the current circumstances, there is a clear risk that a high increase in wages without improved workplace productivity would fuel inflation and increase the likelihood of a steeper rise in interest rates to the detriment of growth and job creation.”
— Innes Willox, CEO of Australian Industry Group
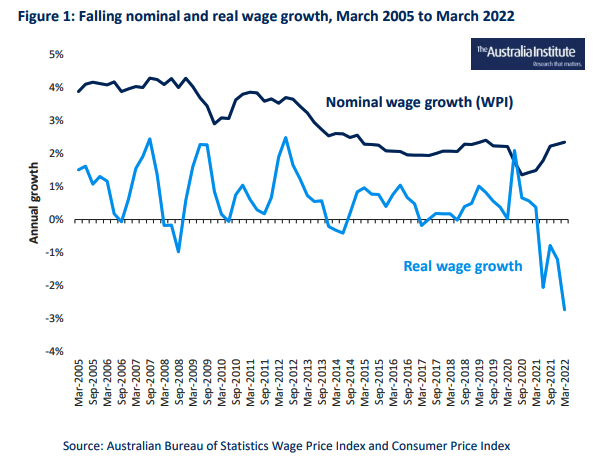
The fear that wage growth has, or could, play a significant role in Australia’s inflation typically ignores the fact that, as shown in Figure 1, real wage growth is at historically low levels and has been for some time.
While wage growth clearly has not been the driving force of recent increases in Australian inflation, or indeed inflation around the world, the continuing impact of COVID 19 and the sharp increase in global energy prices associated with Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine clearly have.
What causes inflation?
Inflation refers to an overall increase in the level of prices in an economy. According to the International Monetary Fund:
Inflation is the rate of increase in prices over a given period of time. Inflation is typically a broad measure, such as the overall increase in prices or the increase in the cost of living in a country.
While much is made of the link between increases in the costs of inputs (such as the price of oil) and increases in prices (such as the price of petrol) in fact many firms have a high degree of discretion about how much, if any, of an increase in costs they will pass on in the form of higher prices.
In short, if firms choose to absorb all of an increase in cost rather than increase prices the cost increases will lead to a reduction in profit not an increase in prices. Similarly, if firms pass on price increases that are more than enough to cover an increase in their production costs then profits will rise. In turn, macroeconomic data on economy-wide changes in prices and the share of GDP flowing to workers and profits can shed light on both the underlying sources of inflation and the distributional consequences of firms’ responses to rising production costs.
While spokespeople for large companies often suggest they have ‘no choice’ but to increase their prices when their costs increase not only do they have the choice to accept lower profits, a closer examination of their language makes clear that they face a range of choices.
For example, in attempting to explain how he had ‘no choice’ but to increase prices in his stores in early 2002, Gerry Harvey, the Executive Chairman of the retail chain Harvey Norman, actually made clear the range of choices he did face:
If a guy down the road drops the price, we drop the price,
If we drop the price, they drop the price.
But if it’s costing you all 10 per cent more than it was yesterday, they’re all going to put up their prices (because) they’ve got no choice.
Mr Harvey makes clear that his company is willing and able to choose to lower prices to match his competitors pricing, even in the absence of a change in cost. He also makes clear that he expects other firms not to absorb any increase in costs and that his firm and his competitors are all likely to increase their prices if costs increase by 10 percent, but it is not clear by how much his firm, or others, would chooses to increase their prices by.
Intriguingly, he ends this explanation by saying firms have no choice, even though all firms have different costs structures and his opening statement is that he would lower his price to match a cheaper offer by a competitor.
As all firms have slightly different cost structures, contract terms for inputs, bottoming costs and exposures to market rents it is inconceivable that all firms in any industry would experience identical changes in price and, in turn, the choices firms make about their price setting in response to changes in cost reflect both their current rates of profit and their willingness to gain or lose market share…..
In short, while in the long run firms must set prices sufficient to cover their costs of production, there is no direct link between costs of production and prices beyond the desire of firms to maintain, or increase, their profits. While firms in new industries seeking rapid growth often deliberately set their prices below their costs in, companies like Santos are currently enjoying a significant increase in price that is entirely unrelated to their cost of production.
Given that profits currently account for a record share of GDP there is simply no truth behind the assertion that the Australian corporate sector has ‘no choice’ but to pass on cost increases in full in the form of higher prices. Indeed, the rising profit share of GDP suggests that Australian firms have, for some time, been choosing to increase their prices faster than their costs have been rising. By definition this causes higher inflation…..
The European Central Bank’s analysis of the role of profits in driving inflation
In a recent speech, Isabel Schnabel, a member of the board of the European Central Bank, said “profits have recently been a key contributor to total domestic inflation” ……
Ms Schnabel went on to state that:
many firms have been able to expand their unit profits in an environment of global excess demand despite rising energy prices… The resilience of profits is particularly evident in those sectors most heavily exposed to global conditions, such as the industry and agricultural sector.
And:
To put it more provocatively, many euro area firms, though by no means all, have gained from the recent surge in inflation. The fortunes of businesses and households have diverged outside of the euro area, too, with corporate profits in many advanced economies surging over the past few quarters.
Poorer households are often hit particularly hard – not only do they suffer from historically high inflation reducing their real incomes, they also do not benefit from higher profits through stock holdings or other types of participation.…..
Australian results
The methodology used by the ECB to decompose recent shifts in price levels and attribute them to shifts in wages, profits and taxes can be applied to Australian data to show the contribution of each to inflation.
The Australia Institute applied the ECB method to annual data for the financial years 2005 to 2021 and quarterly data for June 2021 to March 2022 (the most recent quarter for which data is available). Annual data was used where possible to minimise the volatility in the underlying data caused by COVID-19 support payments affecting tax and subsidies.
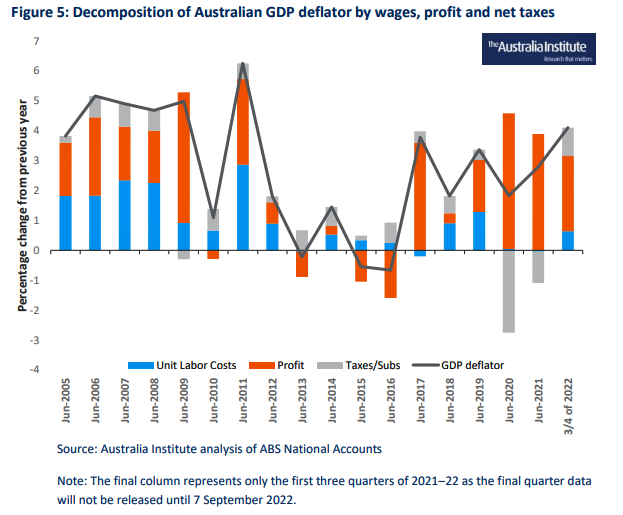
The Australian data provides even more stark results than the ECB’s. Figure 5 shows that unit labour costs played almost no role in inflation (as measured by the GDP deflator) over the period 2013 to 2021 and had typically contributed less than half of the GDP deflator prior to 2013.
For the three quarters of data available for 2021–22, encompassing the current uptick in the CPI, labour costs have played an insignificant role, accounting for only 0.6 percentage points of the 4.1 percentage point increase in the GDP deflator (15 percent of the total).
Meanwhile profits have accounted for 2.5 percentage points of the increase in the GDP deflator (about 60 percent of the total).…..
Read the full 15 page report here.
Billionaire business owners and industry lobbyists have other ways of saying our profits are more important than people without ever mentioning the word. Here is a recent example.
ABC News, 17 July 2022:
Head of the Victorian Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Paul Guerra, welcomed the announcement but said the government must ensure it keeps the balance between supporting people in need and running the economy into debt.
"The federal government has told us the pandemic is not over," Mr Guerra said.
"The current wave seems to be stronger than we might have all first thought so we think it's a good thing that support is being provided there for those who are in need.
"That said, we'd like to make sure they come off as soon as the current risk is over so we can accelerate our way as we recover out of COVID."
BACKGROUND
Across the board record profit taking is not just an Australian phenomenon….
Political economist Assistant Professor Isabella M. Weber speaking on U.S. NPR radio program "All Things Considered", 13 February 2022:
Companies always want to maximize profits, right? In the current context, they suddenly cannot deliver as much anymore as they used to. And this creates an opening where they can say, well, we are facing increasing costs. We are facing all these issues. So we can explain to our customers that we are raising our prices. No one knows how much exactly these prices should be increased. And everybody has some sort of an understanding that, oh, yeah, there are issues, so, yes, of course companies are increasing prices in ways in which they could not justify in normal times.
But this does not mean that the actual amount of price increase is justified by the increase in costs. And as a matter of fact, what we have seen is that profits are skyrocketing, which means that companies have increased prices by more than cost. In the earnings reports, companies have bragged about how they have managed to be ahead of the inflation curve, how they have managed to jack up prices more than their costs and as a result have delivered these record profits. [my yellow highlighting]